Lung Cancer
-
Lung cancer is a death penalty?
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the lungs. Your lungs are two spongy organs in your chest that take in oxygen when you inhale and release carbon dioxide when you exhale.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide.
People who smoke have the greatest risk of lung cancer, though lung cancer can also occur in people who have never smoked. The risk of lung cancer increases with the length of time and number of cigarettes you've smoked. If you quit smoking, even after smoking for many years, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing lung cancer.

-
Solutions in the USA
On a positive note, the number of new lung cancer cases continues to decrease, partly because people are quitting smoking. Also, the number of deaths from lung cancer continues to drop due to people stopping smoking and advances in early detection and treatment.
In the USA lung cancer is treated in several ways, depending on the type of lung cancer and how far it has spread. People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments. People with small cell lung cancer are usually treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy.Solutions in the UK
A new cancer immunotherapy drug is authorized in the UK. The use of the drug nivolumab is already called a breakthrough in the treatment of cancer. Clinical trials have shown that nivolumab stops the spread of skin and lung cancers. Equally important, Nivolumab restores the body's normal immune response.
In one clinical trial, patients were taking already approved nivolumab, and in 58% of patients, cancer had stopped spreading in less than a year.
-
Statistics in the USA
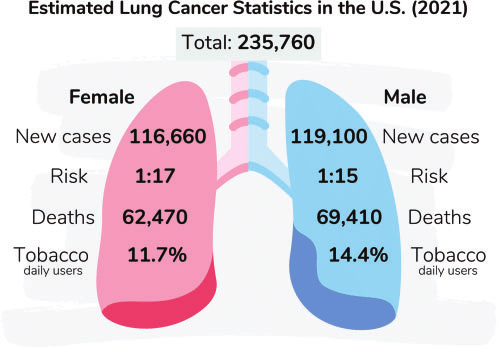
The American Cancer Society’s estimates for lung cancer in the United States for 2021 are:
About 235,760 new cases of lung cancer (119,100 in men and 116,660 in women) About 131,880 deaths from lung cancer (69,410 in men and 62,470 in women) Lung cancer mainly occurs in older people. Most people diagnosed with lung cancer are 65 or older; a very small number of people diagnosed are younger than 45. The average age of people when diagnosed is about 70.
Lung cancer is by far the leading cause of cancer death among both men and women, making up almost 25% of all cancer deaths. Each year, more people die of lung cancer than of colon, breast, and prostate cancers combined.Statistics in the UK
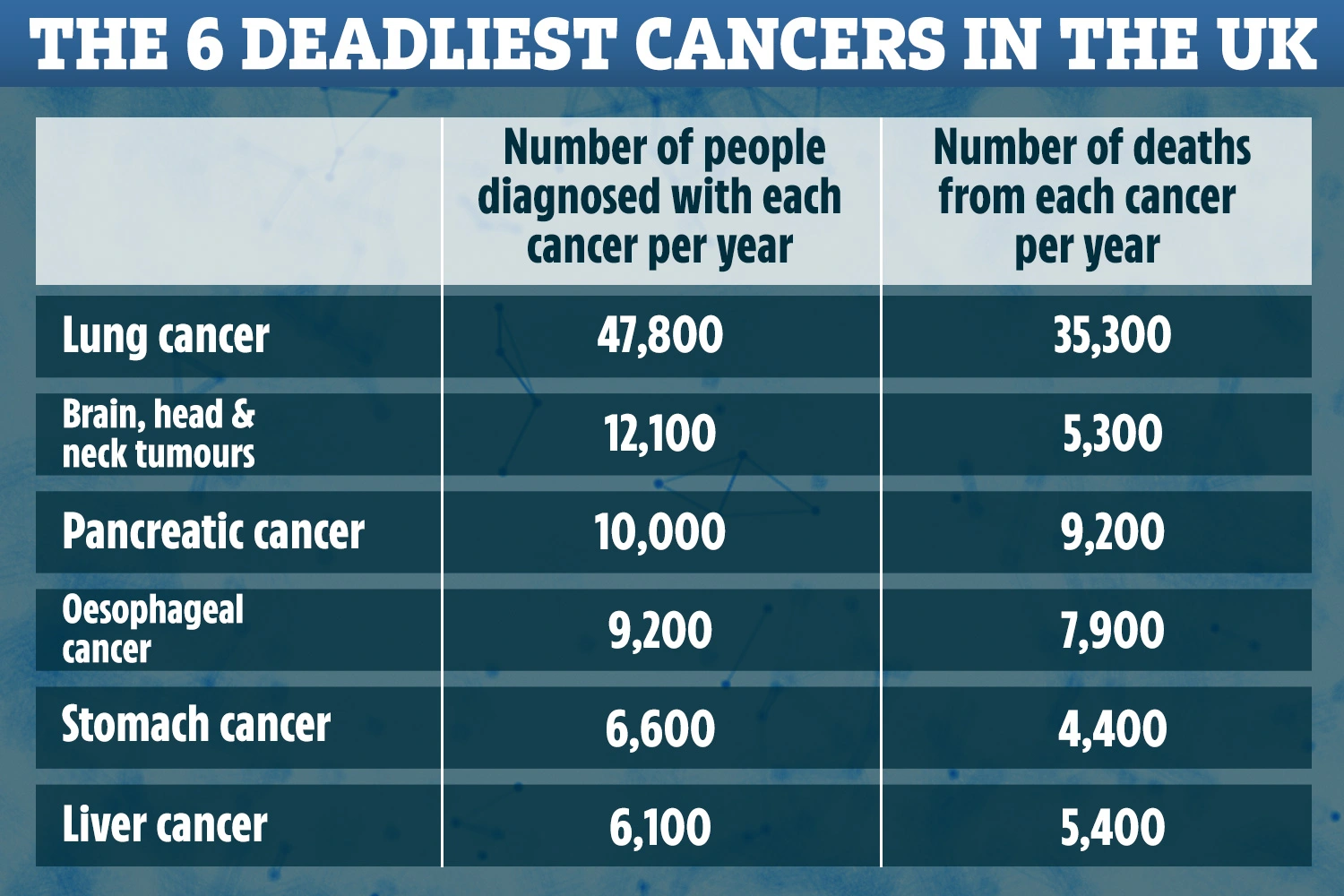
There are around 48,500 new lung cancer cases in the UK every year, that's more than 130 every day (2016-2018).
Lung cancer is the 3rd most common cancer in the UK, accounting for 13% of all new cancer cases (2016-2018).
In females in the UK, lung cancer is the 2nd most common cancer, with around 23,300 new cases every year (2016-2018).
In males in the UK, lung cancer is the 2nd most common cancer, with around 25,300 new cases every year (2016-2018).
Incidence rates for lung cancer in the UK are highest in people aged 85 to 89 (2016-2018).
Each year more than 4 in 10 (44%) of all new lung cancer cases in the UK are diagnosed in people aged 75 and over (2016-2018).